
Modern cars have about 10 times more control units than an average 1990s car. As a result, you can diagnose a lot more issues by simply looking at error codes. This is where on-board diagnostics (OBD2) scanners come in.
You can save lots of time and money if you learn how to use an OBD2 scanner. Here’s everything an average driver needs to know about them.
Used cars have dark secrets
Reveal them all! Just enter a VIN code and click the button:
What does an OBD2 scanner do?
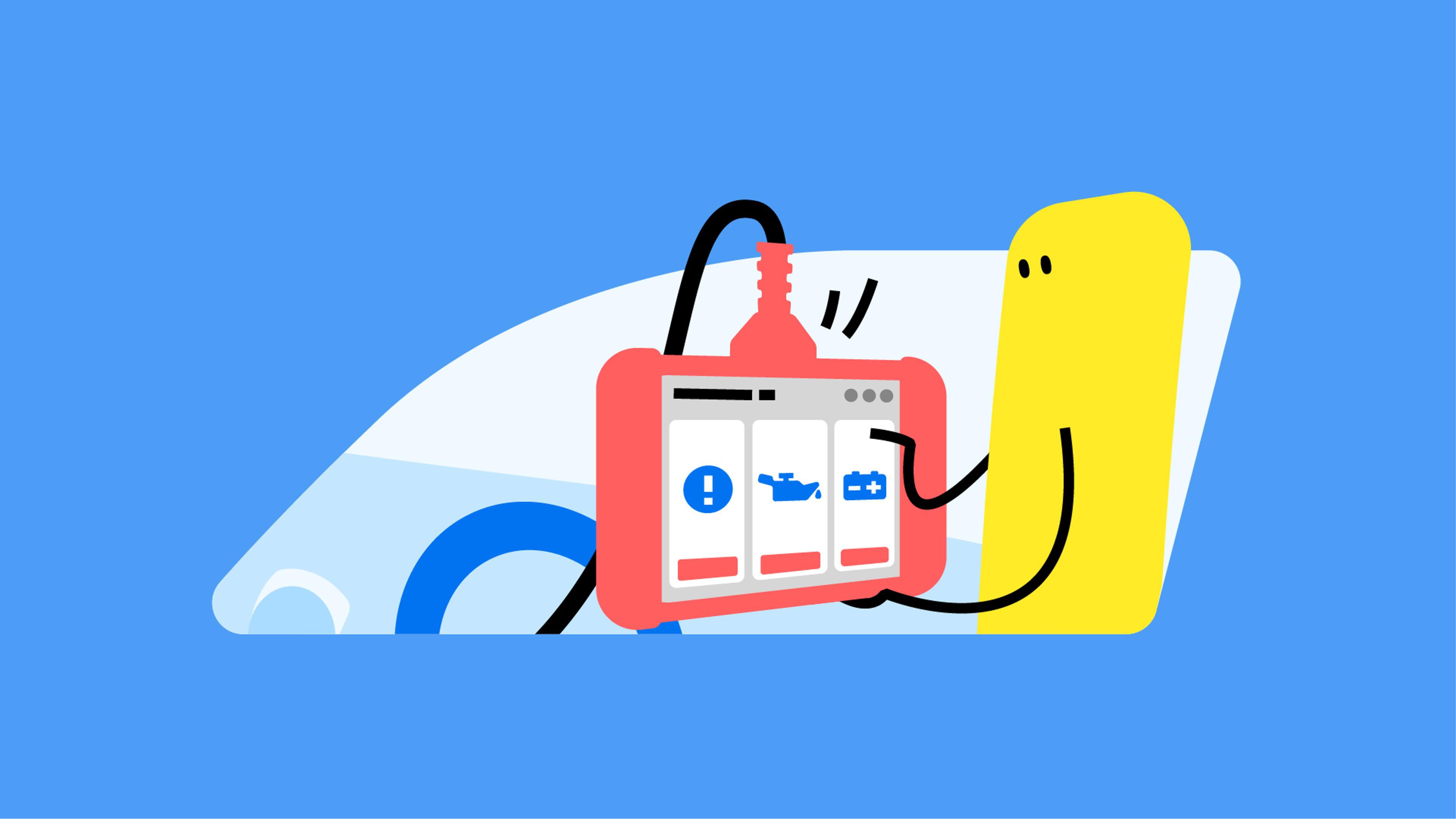
An OBD2 scanner is a powerful tool that plugs into a special port inside a car and collects information from its control units. This includes fault codes and live data, such as pressure, temperature, and speed readings.

All this information comes from various sensors inside the car. Usually, fault codes appear when a reading is over the limit, or a sensor doesn’t respond anymore.
More advanced diagnostic tools can perform various servicing functions and even coding, which is needed when replacing particular parts in modern vehicles.
Modern on-board diagnostics became mandatory in all cars made from 1996 in the United States and from 2004 in Europe.
Types of OBD2 scanners
You can find all kinds of OBD2 scanners on the market today. The most basic and cheapest option is a Bluetooth OBD2 code reader that can be paired with your smartphone. Normally, these only cost a few bucks and can read fault codes and basic live data, making a convenient choice for an average driver.
For those leaning towards DIY repairs, a more expensive OBD2 scanner is a better option because it can also reset service reminders, activate servicing functions for replacing brake pads, and read more live data. These usually start at around $100 and go up depending on capabilities.
Ordinary OBD2 scanners don’t always work for professionals as they have to be prepared for anything from an oil change to replacing an engine. Fault code and live data reading are nothing compared to the vast possibilities of coding and programming in professional OBD2 diagnostic tools.
With the right tools, a professional automotive electrician can adjust every possible option in a modern car. However, these tools cost thousands and are too complicated for a regular user.
How to read OBD2 fault codes
Reading fault codes is the most important step of OBD2 diagnostics. Therefore, if you want to do anything with an OBD2 scanner, this is the first and foremost thing to learn.
The controls of different diagnostic tools vary depending on their model, but the main principle is pretty much the same.
1. Connect the scanner
All modern cars have an OBD2 port that’s usually located under the steering wheel or somewhere in the center console. This port is often hidden underneath a plastic cover, so find it and plug in your OBD2 scanner.
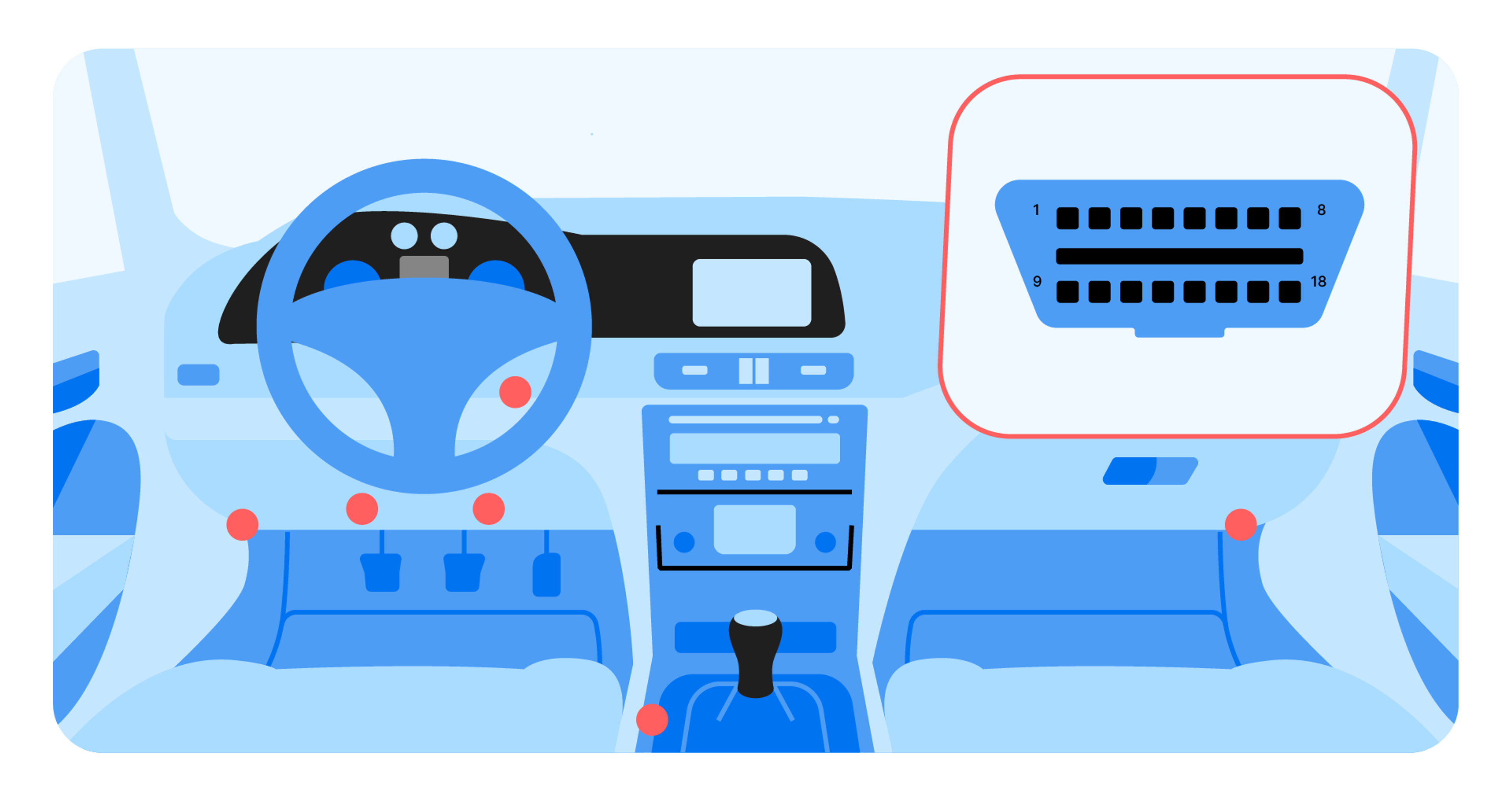
Many modern scanners and code readers use Bluetooth instead of wires, so make sure it’s connected.
2. Turn on the ignition
You can’t perform computer diagnostics on a car if the ignition isn’t on, so turn on the ignition before scanning. Turn off the headlights, radio, and AC to reduce electricity consumption to a minimum.
Most vehicles allow you to scan for fault codes when the engine’s running. Fault codes are stored and won’t disappear until you clear them, but starting the engine is convenient when looking at live data because of various readings.
3. Choose your vehicle
As soon as you connect your OBD2 scanner to a car and turn on the ignition, you can choose your car’s make, model, and specifications. These are necessary for the tool to recognize control units and process readings properly.
Most modern diagnostic tools have an automatic recognition system that automatically reveals a car’s VIN number and sets up all the necessary information for you. Moreover, you can also enter a VIN manually if, for some reason, a scanner doesn’t find it automatically.
4. Scan for fault codes
Finally, choose a fault code reading option. Most scanners let you choose which units you want to scan, also offering a complete scan of all available control units.
If you’re having trouble locating these options, an integrated help page or a user manual should guide you through these steps.
Depending on a car’s model, a full scan should take between a few seconds and a few minutes.
5. Inspect revealed fault codes
These fault codes you see after a scan are the main reason for various warning lights coming up on your instrument cluster. Sometimes fault codes are relatively straightforward, such as “00287 – ABS Wheel Speed Sensor; Rear Right”. It probably means that the rear right ABS sensor needs replacing.
However, the problems behind fault codes are often way more complicated than you may think. For example, “P0171 – System Too Lean (Bank 1)” means that the fuel mixture is too lean, but it can be caused by a clogged fuel filter, a failing fuel pump, a vacuum leak, various sensor failures, and numerous other things.
Pro tip: Reading live data
An ability to read live data is an excellent addition to solving various car problems. Most control units have an additional section for live data, allowing you to monitor it in real-time. How does that help?
Let’s say a car is low on power, and the only fault code that appears is a notification that the vehicle is in limp mode. In that case, you can check whether the fuel and boost pressures, intake airflow, and intake manifold pressures are normal.

However, even with access to all these features, you may need help figuring out the fault codes and sourcing problems.
An essential part of used car buying
Modern used car markets are full of pitfalls for buyers. Used car sellers use the gullibility of buyers to sell cars with a bad history, electrical issues, or even legal problems.
While vehicle history reports can reveal lots of useful information about a car, a proper vehicle inspection is essential if you want to avoid huge repair costs.
Always get a history report and check for fault codes before buying a used vehicle. If you don’t have an OBD2 scanner or still don’t know how to use one, take the car for a professional inspection.

Check your registration number
Avoid costly problems by checking a vehicle's history. Get a report instantly!
How to get rid of fault codes
Scanning for fault codes is a part of diagnosing the car’s problem, therefore, fault codes often won’t reveal issues directly. Even if computer diagnostics show a faulty mass airflow sensor, automotive electricians test the sensor using a multimeter to ensure it’s faulty and avoid replacing the wrong part. You’d be surprised how often such fault codes appear due to damaged wiring, loose connections, and corrosion.
After sourcing the problem, someone must fix it and check for faults again. If it doesn’t appear anymore, the problem is probably solved, and you can hit the road.
Frequently asked questions

Article by
Evaldas Zabitis
Evaldas has been writing since middle school and has had a passion for cars for as long as he can remember. Right after getting his driver’s license, he spent all of his savings on shoddy cars so he could spend time fixing, driving, and selling them. Evaldas is always interested in automotive technical innovations and is an active participant in automotive community discussions.
