11/07/2024
What is NHTSA? Role, initiatives, and vehicle safety ratings

Renata Liubertaitė

Millions of vehicles traverse the roads worldwide, so it's crucial to ensure they meet safety standards. In the US, this burden falls under the NHTSA's responsibilities, yet that's not the only thing they do.
So, what exactly is NHTSA, and how does this agency contribute to transportation safety? Let's find out in this blog post.
What is NHTSA and what does it do?
NHTSA stands for the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, a federal agency within the United States Department of Transportation. Its core mission is to establish and enforce safety standards on American roads to reduce motor vehicle crashes, injuries, and fatalities.
More specifically, NHTSA:
- Sets safety standards for motor vehicles to ensure their compliance with federal regulations.
- Researches various traffic safety issues to better understand the causes of crashes, injuries, and deaths.
- Develops and promotes educational campaigns and initiatives to raise public awareness about safe driving practices and reduce risky behaviors.
- Performs crash tests and evaluates the safety of new vehicles sold in the US.
- Investigates safety-related defects in motor vehicles and related equipment.
- Issues car recalls.
Need help buying a used car?
Enter a VIN code to learn more about any vehicle!
NHTSA vehicle safety standards – what exactly does the agency regulate?
As the key agency for vehicle safety standards in the US, the NHTSA covers various aspects of vehicle design, construction, and performance. These standards are continuously reviewed and updated to keep up with technological advancements, address emerging safety concerns, and improve overall vehicle safety.

Some of the main focus areas of NHTSA include:
- Crashworthiness standards, which ensure that the vehicle can properly protect its occupants in case of an accident. NHTSA works on establishing and enforcing requirements for features such as seat belts, airbags, tires, robust occupant protection structures, and similar.
- Crash avoidance standards that are aimed at preventing crashes or reducing their severity. These standards cover various driver assistance technologies, such as anti-lock braking systems (ABS), forward collision warning, blind spot detection, lane departure warning, and other.
- Tire safety standards that are set to ensure tire durability, performance, and safety.
- Lighting standards are set for maximum visibility on the road, which includes requirements for headlights, taillights, turn signals, and other lighting components.
- Child safety standards, which include requirements for the design, performance, and labeling of car seats.
- Theft prevention standards aim to prevent theft and facilitate the recovery of stolen vehicles. These standards may include requirements for features like immobilizers, alarm systems, and vehicle identification numbers (VINs).
Every car manufacturer must comply with the standards set by the NHTSA to ensure that their vehicles meet minimum safety requirements.
NHTSA safety programs
To achieve its goals, NHTSA also runs various safety programs and initiatives aimed at different aspects of road safety. Here are a few examples to help you get the idea.
NHTSA child safety program
With its child safety program, NHTSA aims to educate parents and caregivers on how to keep children safe in and around a vehicle. Although the agency pays a lot of attention to the proper use of child safety seats, it highlights that safety goes far beyond that.
To prevent injuries and deaths, NHTSA provides tips and educational information through different prevention campaigns. Topics mostly revolve around vehicle features that can help avoid rollaway, backover, heatstroke, injuries caused by power windows, seat belt entanglement, and other dangerous situations that involve chidren.
Older driver safety
NHTSA also works with many national, State, and community partners to provide resources for older drivers, caregivers, health care professionals, etc., that can help increase older drivers’ safety on the road.
The agency offers educational material, including fact sheets and videos, on managing age-related changes in driving ability and tips on how to continue driving safely. For instance, how to adapt a vehicle to meet an older driver’s needs.
Pedestrian and bicyclist safety
To increase the safety of pedestrians and bicyclists, NHTSA runs awareness campaigns and works to improve the infrastructure.
Similarly to its other programs, these campaigns include educational information, tips, checklists, guides, videos, and similar materials that focus on safe and responsible behavior while walking, exercising, or cycling.
NHTSA crash test ratings explained
If you’ve ever researched cars, there’s a great chance you’ve come across NHTSA vehicle safety ratings. The agency conducts various crash tests and safety assessments to evaluate the safety performance of various models and help consumers make more informed decisions.
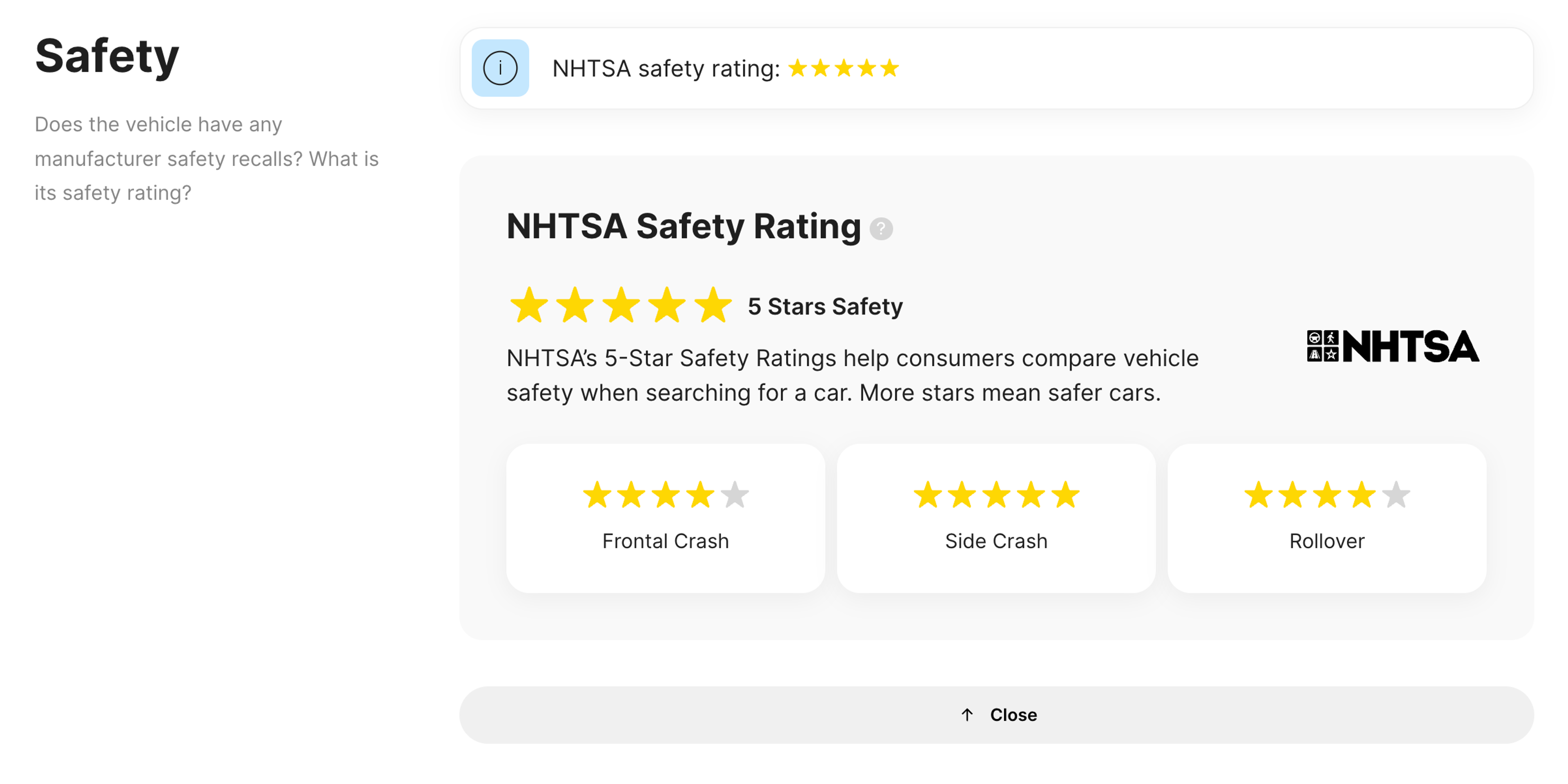
These ratings range from one to five stars, with five stars indicating the highest level of safety:
- 5 stars: Overall injury risk for this vehicle is much less than average.
- 4 stars: Overall injury risk for this vehicle is less than average to average.
- 3 stars: Overall injury risk for this vehicle is average to greater than average.
- 2 stars: Overall injury risk for this vehicle is greater than average.
- 1 star: Overall injury risk for this vehicle is much greater than average.
To calculate the overall safety score, the NHTSA conducts frontal, side, and rollover resistance tests, which account for the majority of crashes on America’s roads.
Frontal crash test

Frontal crash tests simulate a head-on collision between two similar vehicles from the same weight class traveling at 35 mph. The test involves two test dummies – an average-size adult male in the driver’s seat and a small-size adult female in the front passenger seat, both secured with seat belts.
During the simulation, NHTSA measures the forces on these dummies to assess the likelihood of head, neck, chest, and leg injuries.
Side barrier crash test
A side barrier crash test simulates a collision at the intersection, where a car is hit by another vehicle on the driver’s side. Two crash test dummies – an average-size adult male in the driver’s seat and a small-size adult female in the rear passenger seat (driver’s side) – are secured with seat belts and observed during the crash.
For NHTSA's side barrier crash test, the speed is typically set between 31 to 38.5 mph. The vehicle is then propelled sideways into the barrier, simulating a side-impact collision.
Once the crash test is completed, the results are used to determine the likelihood of head, chest, abdomen, and pelvis injuries.
Side pole crash test
A side pole crash test imitates a crash into a static object when a driver slides off the road. This test is conducted using a small-size adult female dummy in the driver’s seat.
During the test, the car is pulled sideways at 20 mph and a 75-degree angle into a rigid 25cm diameter pole.
Side pole crash test results are used to evaluate how likely car occupants are to experience head, chest, lower spine, abdomen, and pelvis injuries in similar scenarios.
Rollover resistance test
NHTSA conducts rollover resistance tests to evaluate a vehicle’s susceptibility to rollover accidents. During this test, the car is driven through a series of abrupt turns at increasing speeds until it reaches a critical tipping point and starts to lift off the ground.
To assess a vehicle’s rollover resistance, NHTSA measures various parameters, such as its track width, center of gravity height, wheelbase length, and other characteristics that affect its stability during sudden maneuvers.
Then, the NHTSA calculates a vehicle's static stability factor (SSF) based on its geometric dimensions and compares it to predetermined threshold values established by regulatory standards.
If the vehicle's SSF falls below the threshold, it is considered to have a higher risk of rollover and may receive a lower rollover resistance rating.
NHTSA and automotive recalls
Car recalls are typically issued when a safety defect or non-compliance with safety standards is identified in a vehicle or its equipment. Recalls can be initiated by the manufacturer or by the NHTSA, which has the authority to investigate potential safety defects.
Manufacturers are required to notify vehicle owners of the recall and provide a way to fix it, often free of charge. This can involve repairing the defect, replacing the defective part, or even refunding the vehicle's purchase price.
NHTSA’s role here is to monitor the recall process and hold manufacturers accountable for addressing safety concerns promptly and effectively. Moreover, the agency significantly contributes to raising public awareness about vehicle safety regarding recalls, as owners are not always aware of potential risks or that their vehicles are even affected.
How to check vehicle safety information
Knowing the vehicle meets all safety requirements can give you peace of mind while driving, especially in potentially dangerous situations. Therefore, checking its safety score or whether it has any active recalls is not only a good idea but also a crucial step to take for your and other passengers’ safety.
Here are a couple of ways to do it.
Check the NHTSA website
You can check a vehicle's safety rating directly on the NHTSA’s website – you only need to enter the car’s manufacturing year, make, or model. If you don’t have a specific model in mind and want to check the safest cars, you can just enter one of those requirements and choose from the list of available vehicles.
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration also maintains a database of recalls where car owners and potential buyers can search for recalls by vehicle make and model or its identification number (VIN).
Get a vehicle history report
For safety information and a more comprehensive overview of a specific vehicle, consider getting a vehicle history report. If NHTSA has tested a vehicle you own or want to buy, the report will provide its overall safety score and scores for each tested area. You will also be able to see recall information (if any) – all in one place.
Getting a vehicle history report is a good option because the information it provides goes beyond just safety ratings and recalls. It typically covers a specific car's past events, including mileage records, damage history, title status, historical photos, and more.
Put simply, while the NHTSA website can provide you with safety information about a chosen model, a vehicle history report can help you uncover weak spots in that specific car you check.

Check your VIN
Avoid costly problems by checking a vehicle's history. Get a report instantly!
One way or another, focus on safety information when looking for a vehicle and make sure you’re buying a car that you can trust.
Frequently asked questions

Article by
Renata Liubertaitė
Renata is a writer with over 8 years of experience in publishing, marketing, and SaaS companies. Writing in various fields and covering highly technical topics has taught her to turn complex things into something everyone can understand. When not writing for carVertical, she loves DIY projects and spontaneous bike rides.
