Symptoms of a bad ignition coil

Evaldas Zabitis
A gasoline engine’s operation is impossible without an ignition coil – when it fails, the vehicle’s performance drops. Knowing how to identify a faulty ignition coil is essential for gasoline car owners, as it improves the driving experience and prevents engine damage.
Instead of hoping it won’t happen to you, let’s go through the basics of what an ignition coil is, how important it is, and how to know when it’s faulty.

Used cars have dark secrets
Reveal them all! Just enter a VIN code and click the button:
What does an ignition coil do?
Ignition coils provide powerful bursts of voltage to jump the gap in spark plugs, thus burning the mixture inside the combustion chamber. Only gasoline engines have ignition coils because diesel ones ignite fuel mixture by compressing it.
An ignition coil acts like a transformer – it converts 12 volts into 20,000-40,000 volts.
Normally, an ignition coil contains 2 sets of copper coils (windings). The first coil has only a few turns of wire as it only charges up the ignition coil, while the second coil has thousands of turns, providing high voltage when charged up.
Types of ignition coils
While the purpose of different ignition coil types is the same, modern engines wouldn’t be as efficient without various ignition system improvements.
Here are the most common types of ignition coils and their properties:
- Canister style. This type of ignition coil is filled with oil and can generate higher voltage. However, it takes up a lot of space and is too slow for modern engines, so it’s mostly found in classic cars.
- Coil pack. Many cars in the 1990s were equipped with a wasted-spark ignition system containing a coil pack and sending voltage via spark plug wires. The main drawback is that spark plug wires often malfunction and cause sparks to hit other metal parts of the engine, decreasing its efficiency.
- Coil-on-plug (COP). As the name implies, each spark plug has a separate ignition coil placed directly on it. This ensures better contact and more precise spark control, making coil-on-plug the most common type of ignition coil in modern cars.
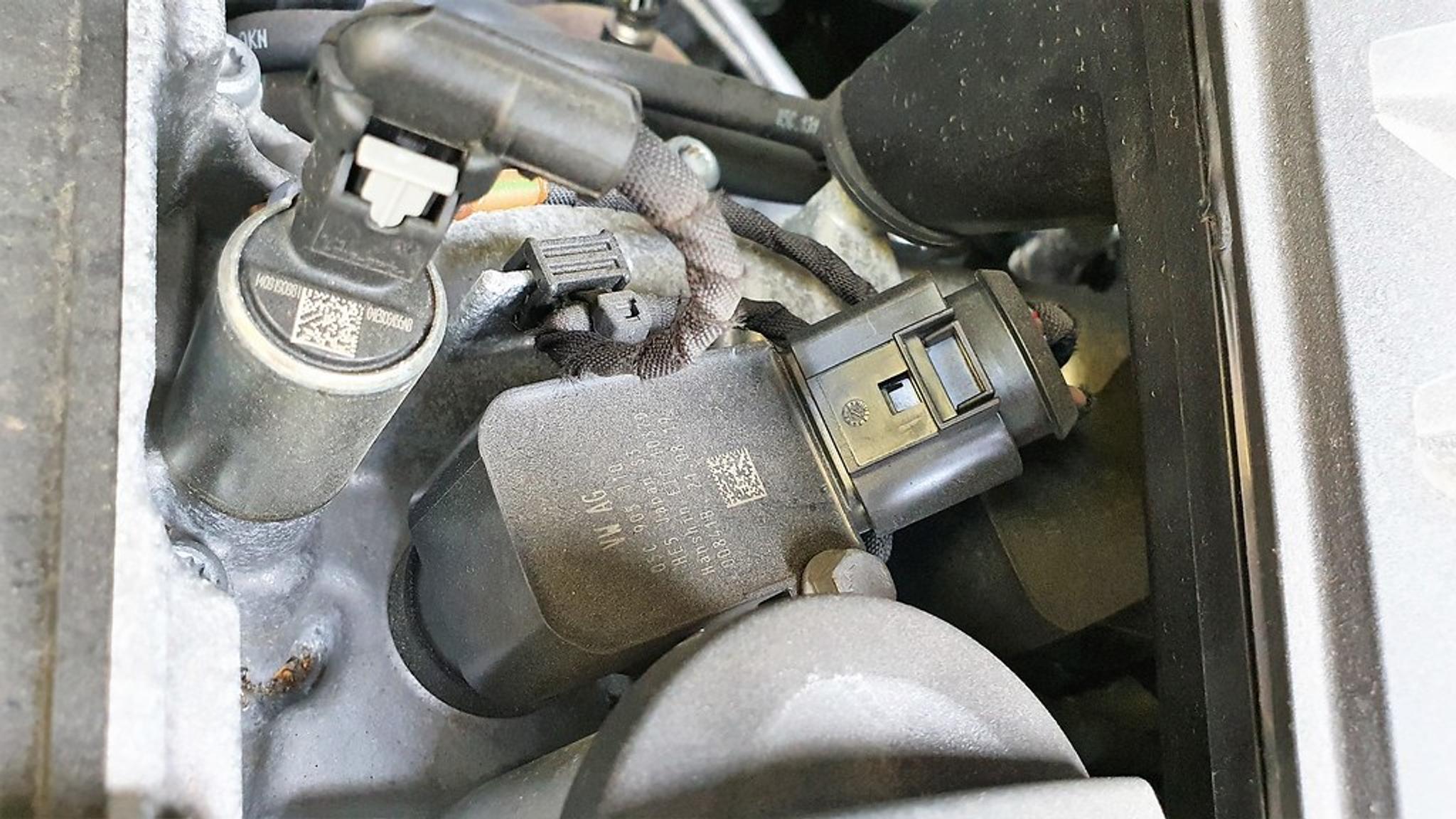

Different ignition coils can cause different issues, so identifying what ignition system is in your car can ease the troubleshooting. When troubleshooting canister-style ignition coils, swapping or replacing them is often the only option. However, modern ignition systems rely on electronic control modules that are compatible with diagnostic tools.
Symptoms of faulty ignition coil
A malfunctioning ignition coil sends distinct signals that are key to preventing further engine damage and other complications. Regardless of the type of coil, the engine will struggle if the ignition coil fails because the fuel mixture won't burn correctly.
From engine misfire to power loss, here are the most common symptoms of a bad ignition coil:
- Engine misfire. You may feel erratic engine behavior if the ignition coil doesn’t provide a consistent spark into a combustion chamber.
- Check engine light. An orange engine-shaped warning light may appear on your dashboard when your car’s engine control module receives unusual readings from various sensors.
- Higher fuel consumption. Ignition, fuel, emission, and many other systems are connected via electrical sensors and control units. As a result, an ignition coil can affect fuel consumption.
- Poor engine efficiency. Since your engine doesn’t burn fuel properly, it may cause vibration, idle roughly, stall, and lack power.
- Engine backfiring. You may notice loud popping noises from the exhaust. This happens when spark plugs don’t ignite fuel properly, causing the burning fuel to get into the exhaust.
- Engine hard starting/not starting. Since faulty ignition coils don’t ignite fuel properly, they can aggravate the engine starting.
- Fuel smell. Faulty ignition coils can cause a rich fuel mixture, meaning that you may smell fuel when the engine is running. Bear in mind that you should never feel this smell inside or outside the car.
The intensity of these symptoms depends on how bad your ignition coils are. Usually, ignition coils fail due to old age, but excessive vibration and extreme heat can also have a big impact.
Related components
These symptoms don’t necessarily mean that the problem is the ignition coil. Modern ignition systems consist of many components to ensure better efficiency and precision, often causing various issues.
The good thing is that finding the problem isn’t that complicated, especially when you’re already troubleshooting it yourself and are ready to get your hands dirty. The trick is to know which components are related and how to check them.
Spark plugs
Normally, every gasoline internal combustion engine has one spark plug per cylinder that generates a spark out of voltage sent from the ignition coil.
Spark plugs have a huge effect on the engine’s performance, therefore, the first thing that many mechanics recommend doing after noticing engine performance issues is changing the spark plugs. Since spark plugs can last as little as 20,000 miles, this suggestion often helps.
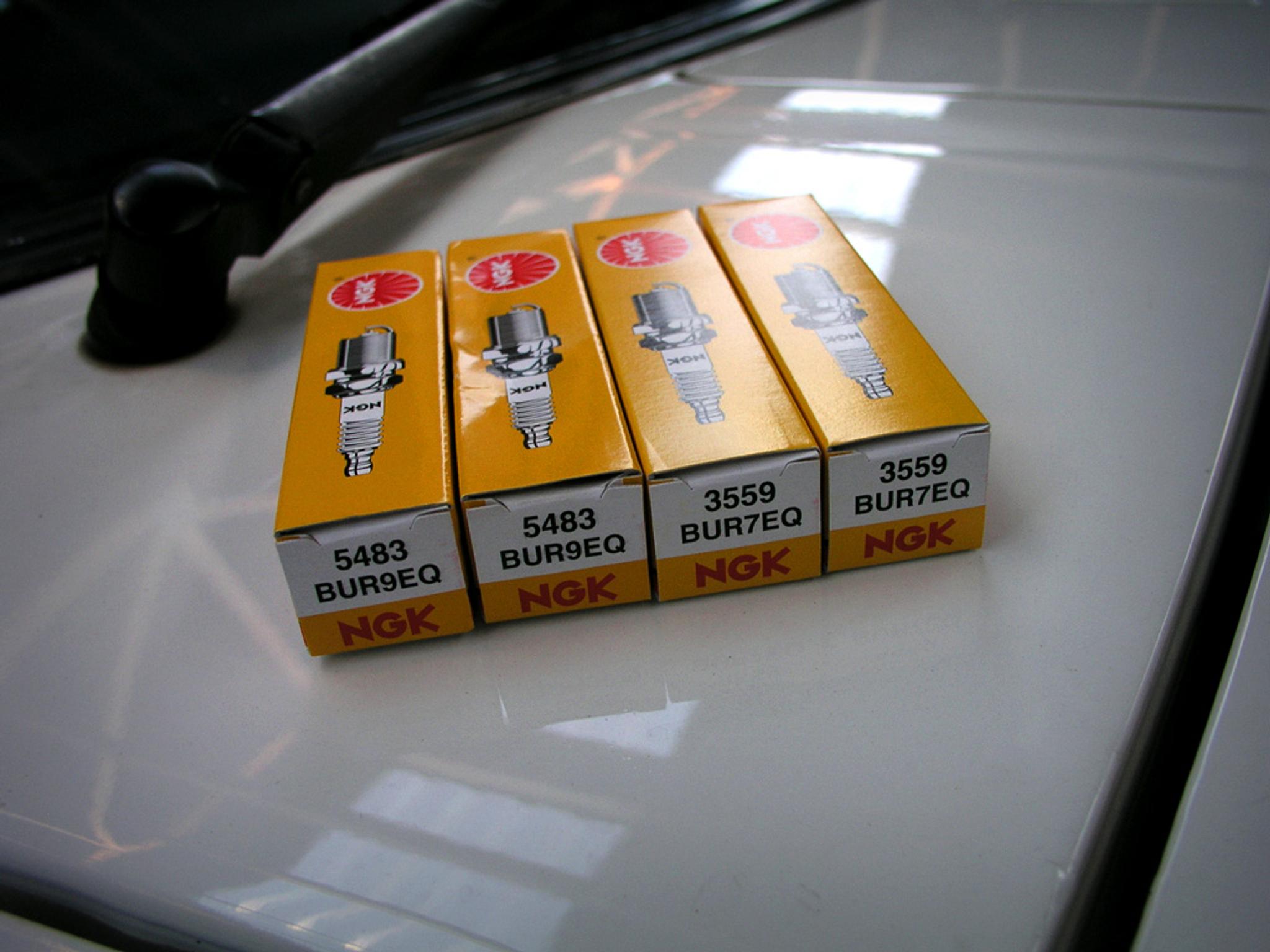

Spark plugs deteriorate faster when poor-quality fuel is used, or the engine isn’t maintained properly. Usually, changing spark plugs isn’t complicated: just take off the spark plug wires of the ignition coil, unscrew the spark plug, and screw in the new one. Be careful not to drop tools or other objects into the cylinder!
Spark plug wires
Many older cars have spark plug wires that connect spark plugs with the ignition coil. These wires were ditched in later models thanks to coil-on-plug style ignition coils. Their main issue is that high voltage may not reach the spark plug properly, often jumping sparks to other metal parts and taking more time.
You can check the spark plug wires yourself. First, perform a visual inspection – make sure there are no cracks or other damage. Then, wait till it’s completely dark outside, open the hood, and start the engine – you should notice if sparks jump to metal parts, such as the engine cover, clips, and bolts. Changing these wires is a simple plug-and-play operation.
Electrical sensors
Modern ignition systems rely on crankshaft and camshaft position, knock, and various other electrical sensors to generate voltage precisely and efficiently. Over time, electrical sensors fail, especially if there are problems with the battery or other electrical components.
Usually, faulty electrical sensors trigger a check engine light and a fault code, therefore, computer diagnostics can help you deal with such problems. You can get a basic OBD-II diagnostic tool for under $100, which would be handy for revealing current faults and troubleshooting.
Ignition control module
All the data processing from electrical sensors and voltage supply control happens inside the ignition control module, which is the brain of the system. If you have a pre-2000s vehicle, it may not have a control module for this system, but all modern cars have it, and problems happen.
Anything from the engine misfire to hard starting can mean a faulty ignition control module. However, don’t make such assumptions early on because a control module replacement is usually a complicated and expensive job.
The good thing about troubleshooting it is that most fault code readers should show something like “control module fault,” meaning that it needs replacing or repairing. Just make sure the spark plugs, ignition coil, electrical sensors, and wiring are intact before spending your money on a new control unit.
Maintenance, lifespan, and replacement of ignition coil
The longevity and efficiency of an ignition coil don't just hinge on its build quality but also on operation and maintenance. Brand-new, high-quality ignition coils can cost around $200 each, so you want to make sure they last as long as possible.
How long do ignition coils last?
While the longevity of ignition coils depends on various factors, they normally last around 100,000-120,000 miles or 5-7 years. Genuine parts can last even longer, especially in well-maintained cars.
Many people drive even higher-mileage cars without ever replacing a single ignition coil. That’s often the result of getting used to decreased efficiency because people often drive their cars with randomly misfiring cylinders without knowing that their car should be more economical and powerful.
This is especially important when you’re buying a used car. If it has over 100,000 miles on the odometer, the car may be sluggish if it hasn’t been maintained well. Therefore, always ask the seller what maintenance has been done over the years. On the other hand, if it’s a low-mileage car, but it doesn’t feel or look like one – the mileage may be fake.
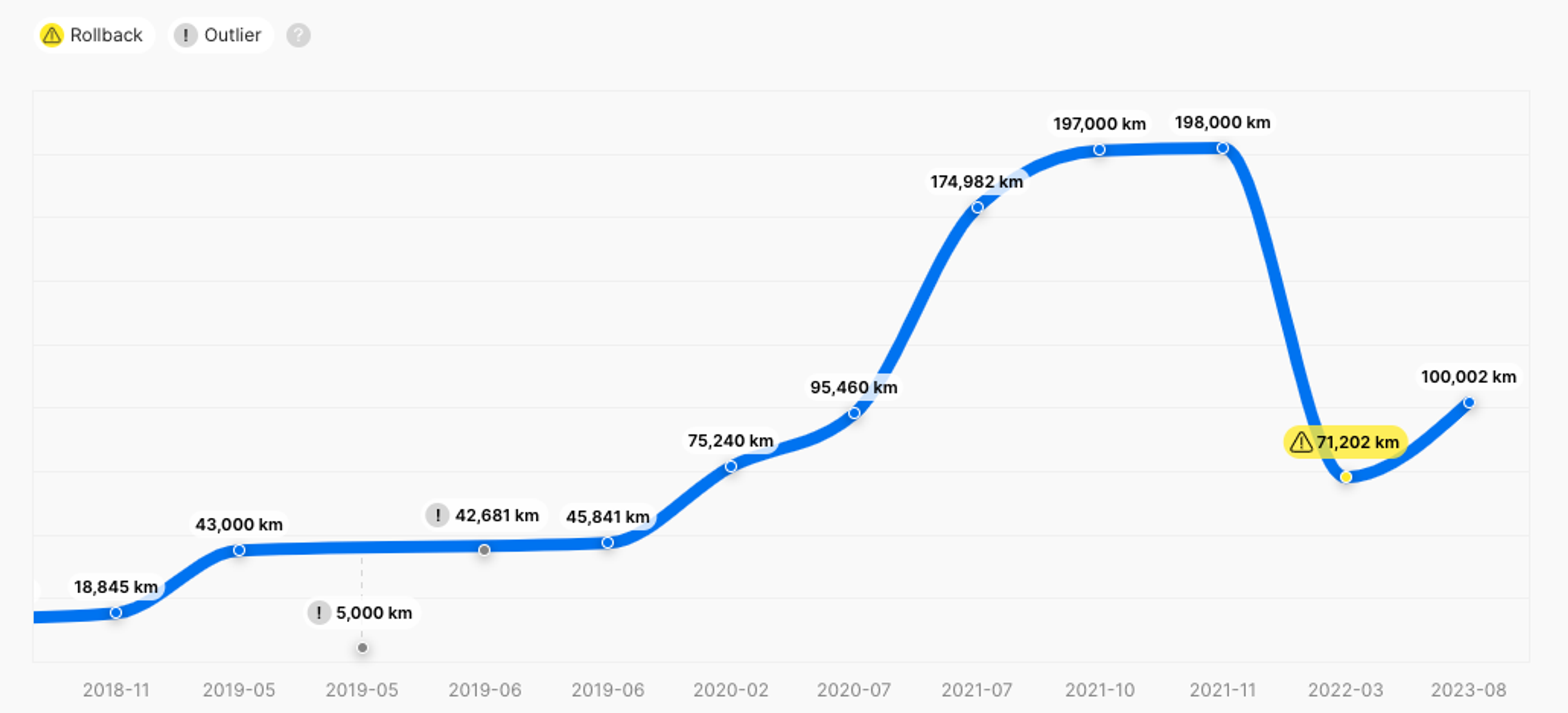
You can reveal mileage fraud, previous damage, theft records, ownership changes, and other critical information about the vehicle’s past by getting carVertical’s full history report. All you need is the vehicle’s VIN number, and you’ll be able to get the report in a few clicks.

Check your VIN
Avoid costly problems by checking a vehicle's history. Get a report instantly!
How to expand the lifetime of ignition coils
Since ignition coils are electrical components, there are no specific procedures to extend their life. However, extreme temperatures, excessive vibration, and moisture are some of the most common aspects that reduce the longevity of ignition coils apart from aging.
So, make sure the engine mounting bushings are in good condition, check if the ignition coils are properly installed, change the oil on time, and don’t overheat the engine.
Frequently asked questions

Article by
Evaldas Zabitis
Evaldas has been writing since middle school and has had a passion for cars for as long as he can remember. Right after getting his driver’s license, he spent all of his savings on shoddy cars so he could spend time fixing, driving, and selling them. Evaldas is always interested in automotive technical innovations and is an active participant in automotive community discussions.
